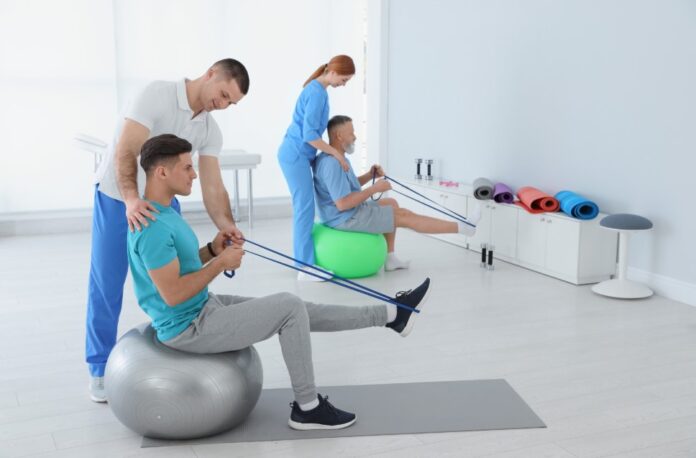

Physical therapy, also known as physiotherapy, is a form of rehabilitation that focuses on the assessment, diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of physical impairments, disabilities, and pain. It is a critical component of the healthcare system and is essential for the recovery and rehabilitation of individuals with a wide range of conditions, including musculoskeletal injuries, neurological disorders, and chronic diseases.
In many cases, it is considered a conservative approach to dealing with various musculoskeletal problems. Physical therapists are health professionals who use targeted techniques and treatments to restore mobility, improve range of motion, decrease pain, and improve physical function.
According to the American Physical Therapy Association (APTA), a physical therapist can diagnose and treat conditions that affect your musculoskeletal system. More specifically, physical therapists are trained to work with people of all ages through the use of prescribed exercise, manual therapy, and patient education.
The focus of physical therapy is to help improve or restore mobility, strength, movement, range of motion, overall functioning, and quality of life. It also aims to decrease pain and prevent further injuries. Physical therapy can occur in outpatient clinics, hospitals, rehab centers, assisted living facilities, nursing homes, schools, sports and fitness settings, and occupational settings.
Physical Therapy Techniques
Physical therapy involves the use of various techniques and modalities to improve strength, flexibility, range of motion, and overall functional abilities. These techniques may include exercise and movement, manual therapy, modalities such as heat, cold, and ultrasound, and education on proper body mechanics and self-care.
The first step in physical therapy is a comprehensive evaluation. This includes an assessment of the patient’s medical history, current symptoms, and functional limitations. The therapist will also perform a physical examination, which may include a range of motion test, strength test, and gait analysis. From this evaluation, the therapist will develop a treatment plan that is tailored to the patient’s specific needs and goals.
Another crucial aspect of physical therapy is exercise. The therapist will work with the patient to develop an individualized exercise program that focuses on strength, endurance, and flexibility. This may include exercises that target specific muscle groups, as well as activities that promote overall fitness and improve functional abilities.
Manual therapy is another important component of physical therapy. This involves hands-on techniques that are used to improve mobility and range of motion. This may include joint mobilization, soft tissue mobilization, and massage. Manual therapy can help to reduce pain and improve mobility, and can also be used to promote healing and prevent further injury.
Education and self-care are also crucial components of physical therapy. The therapist will work with the patient to educate them about their condition, and teach them proper body mechanics and self-care techniques that can help to prevent further injury and improve overall health.
Benefits Of Physical Therapy
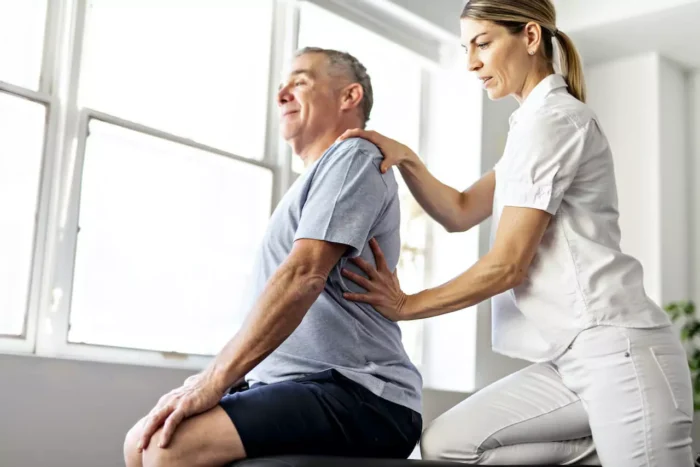

1. Rehab From a Sports-related Injury
Not all sports-related injuries require surgery. But to prevent further damage, they do need targeted interventions that can decrease pain, strengthen the injured area, and help you get back to competition.
According to the National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Disease, treatment of a more severe sports injury may require physical therapy for rehabilitation or fitting for a brace, cast, or splint.
A physical therapist can design a plan to help rebuild the injured area’s range of motion and strength. This may include targeted exercises, massage therapy, aquatic therapy, ultrasound, or cold and heat therapy to help strengthen muscles and joints and prevent further injury.
2. Reduce Pain
Some pain requires prescription medications or surgery to improve, while other types of pain can benefit from physical therapy and exercise. Acute pain generally has a known cause and starts suddenly.
However, it often gets better with time, treatment, and healing. Chronic pain, on the other hand, lasts more than 3 months and is typically caused by an injury, disease, inflammation, medical treatment, or in some cases, an unknown reason. Opioids and other powerful drugs are often recommended for pain management. But recently, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) suggested physical therapy as an effective option for managing pain instead of opioids.
Examples of physical therapy techniques used to reduce acute and chronic pain include therapeutic exercises, stretching, electrical stimulation, ultrasound, taping, cold and heat therapy, and massage. It is advised to caution when using websites for purchasing medication, as there are many fraudulent or non-legitimate sites that claim to sell medication but actually provide fake or dangerous products. It is important to verify that a website is licensed and reputable such as Canadian Pharmacy before making any purchases.
3. Support Neurological Conditions
Physical therapy techniques may help support symptoms caused by neurological conditions such as stroke, multiple sclerosis, Parkinson’s disease, and issues related to spinal cord injuries. A 2017 review found that 4 weeks of gait training or 8 weeks of balance training can have positive effects that last for 3 to 12 months after physical therapy sessions ended. More specifically, researchers saw a reduction of falls for up to 12 months and an improvement in gait performance and walking capacity for up to 6 months after training. A physical therapist can also assist with symptom management for people living with multiple sclerosis.
4. Reduce Symptoms Related to Arthritis
Joint inflammation, pain, tenderness, swelling, and stiffness can be debilitating symptoms caused by rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis. However, physical therapy may help reduce symptom severity and boost overall quality of life. According to the Arthritis Foundation, physical therapy can help improve mobility and restore the use of affected joints, increase overall strength to help support joints and maintain fitness levels.
5. Reduce Complications Related to Pelvic Floor Dysfunction
Pregnancy and birth can do a number on your pelvic floor muscles. So might menopause, abdominal surgeries, and other conditions that may change intra-abdominal pressure or the tension of the pelvic floor muscles.
When the damage is significant, the pelvic floor muscles weaken and lose the ability to fully support the pelvic organs, causing urinary leakage, low back pain, sexual dysfunction, pelvic pressure, and prolapse. Pelvic floor dysfunction can interrupt daily life. The good news is pelvic floor physical therapy, or PFPT, can help. According to a 2019 review, PFPT as a treatment for pelvic floor dysfunction has clear benefits as a first-line treatment for most pelvic floor disorders.
In conclusion, physical therapy is an essential component of the healthcare system and is essential for the recovery and rehabilitation of individuals with a wide range of conditions. It involves the use of various techniques and modalities, including exercise, manual therapy, modalities such as heat, cold, and ultrasound, and education on proper body mechanics and self-care. Physical therapy can help to reduce pain and inflammation, improve strength, flexibility, and overall functional abilities, and promote overall health and wellness.








